Science/grade 8 / Midterm Review/ Beta Radiation Consists of Particles That Are Identical to?
The five states of matter: Definition and phases of change

Each of the five states of matter collectively make up all the "stuff" that'southward in the universe- — everything that takes upwards space and has mass is matter.
All matter is made upward of atoms, which are in turn fabricated upwards of protons, neutrons and electrons.
Atoms come together to form molecules, which are the building blocks for all types of matter, according to Washington State University. Both atoms and molecules are held together by a form of potential energy called chemic energy. Unlike kinetic energy, which is the energy of an object in motion, potential energy is the free energy stored in an object.
Related: How many atoms are in the observable universe?
There are four natural states of matter: Solids, liquids, gases and plasma. The 5th state is the man-fabricated Bose-Einstein condensates.
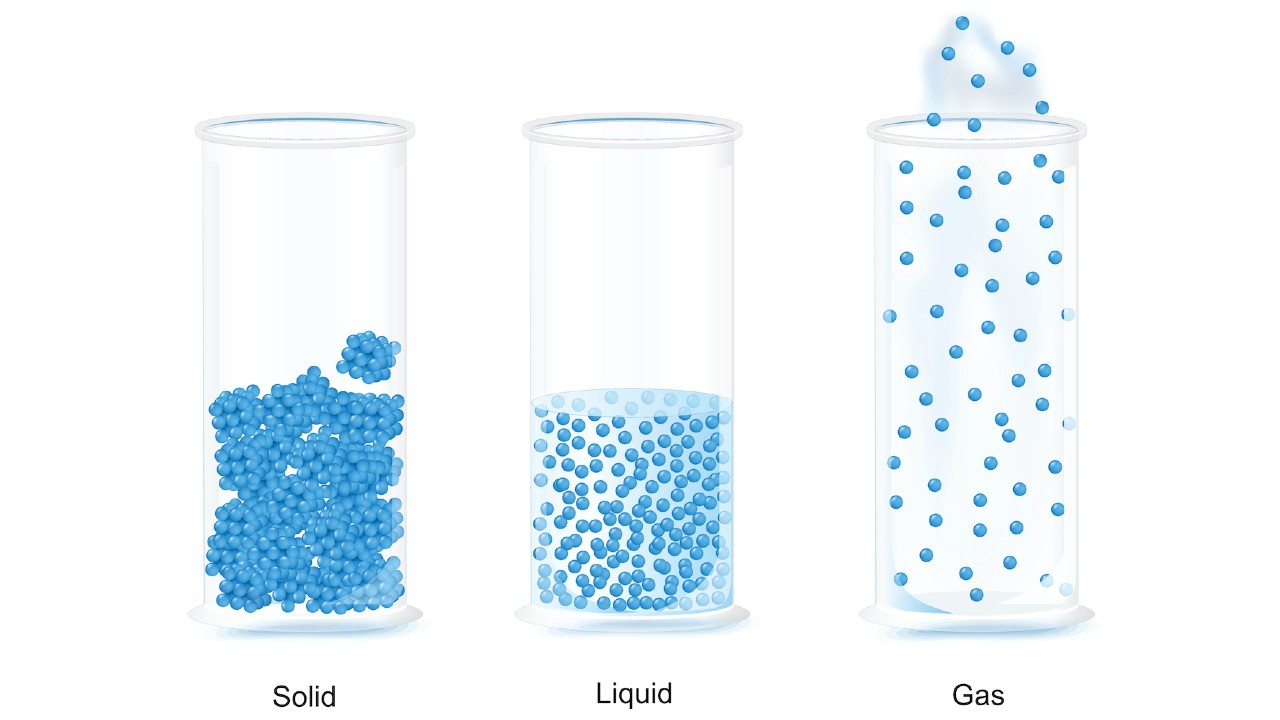
Solids, liquids and gas
In a solid, particles are packed tightly together then they don't motility much. The electrons of each atom are constantly in motion, so the atoms have a small vibration, merely they are fixed in their position. Because of this, particles in a solid have very low kinetic energy.
Solids take a definite shape, likewise as mass and volume, and do non conform to the shape of the container in which they are placed. Solids also take a loftier density, meaning that the particles are tightly packed together.
In a liquid, the particles are more loosely packed than in a solid and are able to flow around each other, giving the liquid an indefinite shape. Therefore, the liquid will conform to the shape of its container.
Much like solids, liquids (about of which have a lower density than solids) are incredibly difficult to compress.
In a gas, the particles have a great deal of space between them and have high kinetic energy. A gas has no definite shape or book. If unconfined, the particles of a gas volition spread out indefinitely; if confined, the gas will expand to fill its container. When a gas is put under pressure by reducing the book of the container, the space between particles is reduced and the gas is compressed.

Plasma
Plasma is not a common state of matter here on Earth, just information technology may exist the near common country of thing in the universe, co-ordinate to the Jefferson Laboratory. Stars are essentially superheated balls of plasma.
Plasma consists of highly charged particles with extremely loftier kinetic free energy. The noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon and radon) are often used to make glowing signs by using electricity to ionize them to the plasma state.
Related: What is dark thing?
Bose-Einstein condensate
The Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) was created by scientists in 1995. Using a combination of lasers and magnets, Eric Cornell and Carl Weiman, scientists at the Joint Institute for Lab Astrophysics (JILA) in Bedrock, Colorado, cooled a sample of rubidium to within a few degrees of absolute zero, equally Live Science has previously reported. At this extremely low temperature, molecular move comes very shut to stopping. Since there is almost no kinetic energy being transferred from one atom to another, the atoms begin to clump together. In that location are no longer thousands of separate atoms, simply one "super atom."
A BEC is used to study quantum mechanics on a macroscopic level. Light appears to wearisome downward as it passes through a BEC, assuasive scientists to study the particle/wave paradox. A BEC likewise has many of the backdrop of a superfluid, or a fluid that flows without friction. BECs are also used to simulate conditions that might exist in black holes.
New states of matter
Research has shown that there may be other states of affair that need further exploration. For example, in January 2021, research published in the journal PNAS revealed that during the transformation betwixt the state of liquid and solid, glass becomes a new state of thing referred to every bit liquid glass.
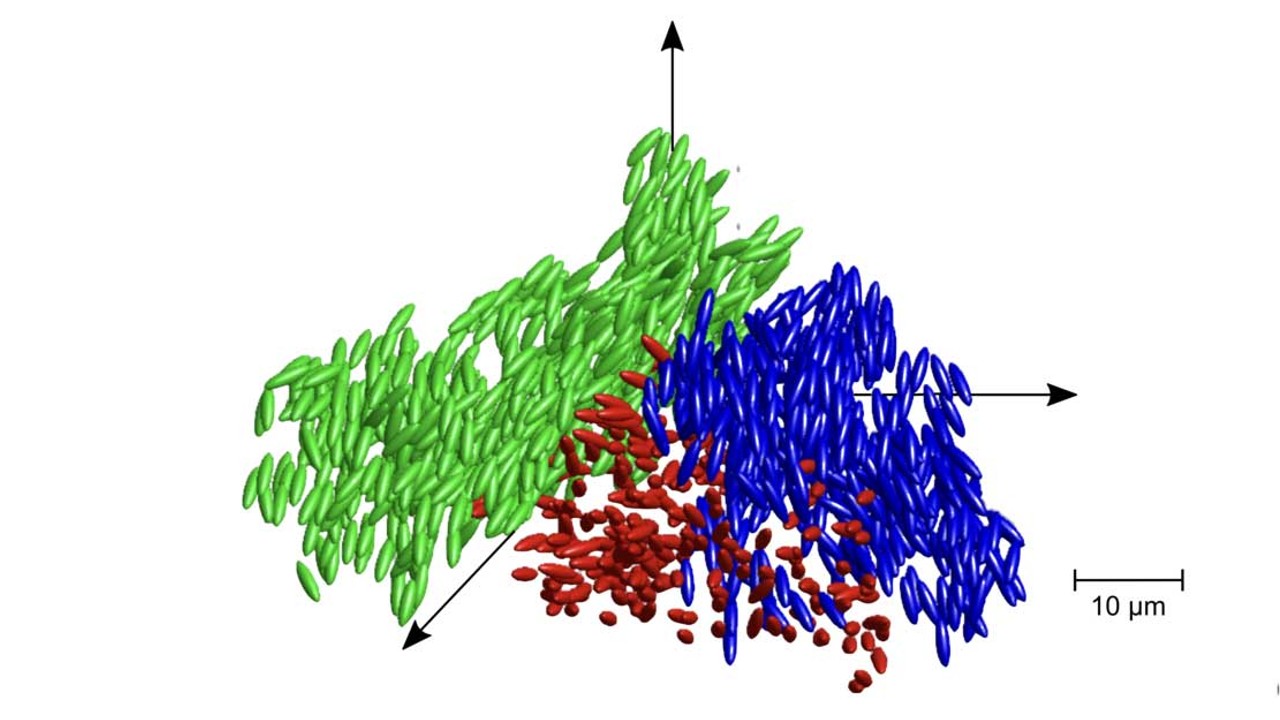
On a microscopic level, liquid glass is somewhere betwixt a solid and a gel-like substance called a colloid — a mixture of particles that are larger than a single atom or molecule. When a substance transforms from a liquid to a solid, molecules are arranged in a crystalline structure — for glass, this doesn't happen and particles are frozen in place before crystallisation occurs. The particles in liquid glass — still -are more flexible than solid drinking glass, only tin not rotate, according to the researchers.
"Our experiments provide the kind of bear witness for the interplay betwixt critical fluctuations and glassy arrest that the scientific community has been after for quite some fourth dimension," senior author of the study and Professor of Soft Condensed Matter Theory at the University of Konstanz Matthias Fuchs, said in a argument.
Related: How do you weigh an atom?
How states of matter change
Adding or removing energy from matter causes a concrete change as matter moves from one state to another. For example, adding thermal energy (heat) to liquid water causes it to get steam or vapor (a gas). And removing energy from liquid water causes information technology to become ice (a solid). Physical changes can also be caused past motion and pressure, according to the Abridged Science for Loftier Schoolhouse Students by H.Messel.
Melting and freezing
When heat is practical to a solid, its particles begin to vibrate faster and move farther autonomously. When the substance reaches a certain combination of temperature and pressure, its melting point, the solid will begin to melt and turn into a liquid.

When two states of affair, such as solid and liquid, are at the equilibrium temperature and force per unit area, additional rut added into the system will not cause the overall temperature of the substance to increase until the entire sample reaches the same physical state, according to Encyclopaedia Britannica. For instance, when you put water ice into a glass of water and leave information technology out at room temperature, the ice and water will somewhen come up to the same temperature. As the ice melts from rut coming from the water, it will remain at 32 degrees Fahrenheit (0 degrees Celsius) until the entire water ice cube melts earlier continuing to warm.
When heat is removed from a liquid, its particles dull downwards and begin to settle in ane location inside the substance. When the substance reaches a absurd enough temperature at a certain pressure, the freezing signal, the liquid becomes a solid.
Sublimation
When a solid is converted straight into a gas without going through a liquid phase, the process is known as sublimation. This may occur either when the temperature of the sample is rapidly increased beyond the boiling point (flash vaporization) or when a substance is "freeze-dried" past cooling information technology nether vacuum conditions so that the water in the substance undergoes sublimation and is removed from the sample, according to the U.Southward. Geological Survey. A few volatile substances will undergo sublimation at room temperature and pressure level, such as frozen carbon dioxide, or dry out ice.

Vaporization
Vaporization is the conversion of a liquid to a gas and can occur through either evaporation or boiling, co-ordinate to Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Considering the particles of a liquid are in constant motion, they frequently collide with each other. Each collision as well causes energy to be transferred, and when enough free energy is transferred to particles near the surface they may be knocked completely away from the sample as free gas particles. Liquids cool as they evaporate because the energy transferred to surface molecules, which causes their escape, gets carried abroad with them.
Liquid boils when enough heat is added to a liquid to cause vapor bubbles to course below the surface. This boiling point is the temperature and pressure at which a liquid becomes a gas.
Condensation and degradation
Condensation occurs when a gas loses energy and comes together to form a liquid, co-ordinate to the U.S. Geological Survey. For case, water vapor condenses into liquid water, known as its dew betoken.
Deposition occurs when a gas transforms direct into a solid, without going through the liquid phase. H2o vapor becomes water ice or frost when the air touching a solid, such as a blade of grass, is cooler than the residue of the air.
Boosted resources
- Picket: Creation of a Bose-Einstein condensate, from the National Institute of Standards and Engineering science.
- Acquire where the matter in the universe came from, from Cornell University'due south Ask an Astronomer.
- Read more about matter, elements and atoms, from the Khan Academy.
This article was updated on Dec. 9, 2021, by Scott Dutfield .
Source: https://www.livescience.com/46506-states-of-matter.html
0 Response to "Science/grade 8 / Midterm Review/ Beta Radiation Consists of Particles That Are Identical to?"
Post a Comment